What is the Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Station?
The Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Station stands as a testament to Japan's resilience and innovation in the energy sector.
0/0

The Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Station (KNPS), while currently not in operation, has taken key
lessons from past events and is undergoing extensive efforts to ensure a safe and responsible
restart.
Following the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Accident, the importance of strengthening nuclear
safety became clearer than ever. The lessons learned from that event have driven significant
advancements at KNPS, reinforcing a commitment to robust risk management and preparedness. As a result,
KNPS has implemented extensive multi-layered safety measures based on TEPCO's "defense-in-depth"
philosophy. These enhancements are designed to mitigate risks of power outages, necessity of reactor
cooling and dispersion of radioactive substances caused by natural disasters such as earthquakes and
tsunamis.
A key aspect of these safety advancements has been the role of third-party observations. Independent
assessments by Japanese and international experts, including visits by organizations such as the Nuclear
Reform Monitoring Committee (NRMC) and the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), have validated
KNPS's progress and reaffirmed TEPCO's commitment to transparency, accountability, and continuous
improvement. TEPCO welcomes these visits as an essential component of responsible nuclear management,
ensuring that the highest safety standards are upheld remains strong and acquiring public confidence in
KNPS.
A critical component of KNPS's safety assurance is the oversight provided by the Nuclear Reform
Monitoring Committee (NRMC). NRMC is an advisory body to TEPCO Holdings' Board of Directors, established
to ensure the effective implementation of nuclear reform efforts. Comprising domestic and international
experts, the committee provides oversight and supervision from an external perspective. Through
continuous observations and guidance, the committee plays a key role in ensuring that KNPS meets the
highest safety standards.
For further details, please visit the NRMC official page
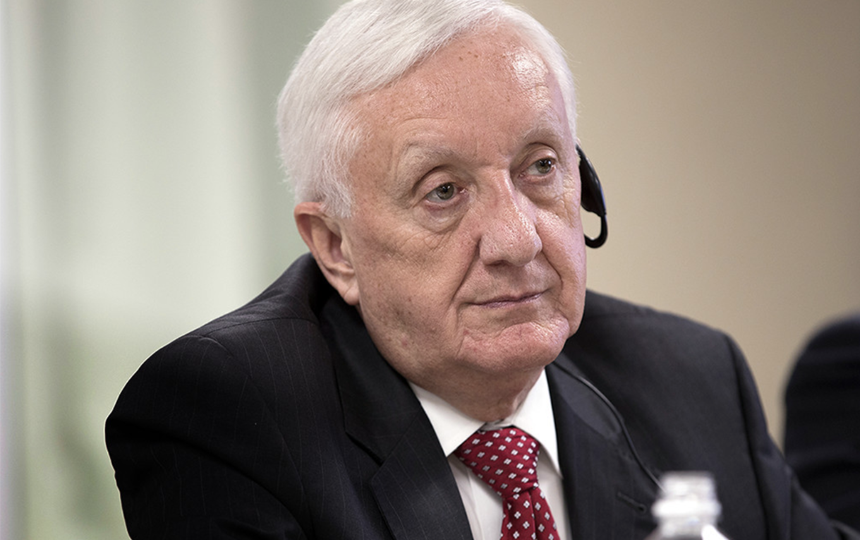
Chairman of the Nuclear Reform Monitoring Committee (NRMC), an advisory body to TEPCO's board of Directors, and former chairman of the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission. The NRMC has been assessing the security and safety of KNPS for 13 years. In December 2024, the committee visited the station to observe a general emergency exercise and review the command system.

A comprehensive review of KNPS was conducted between May 13 and May 17, 2024, by a team that included a
representative from the NRMC. This detailed inspection, which focused on Unit 7 as an exemplar of the
station's overall progress, concluded that KNPS has made significant advancements in safety and
operational readiness. The findings reaffirmed that no critical issues were identified, reinforcing
confidence in the station's preparedness.
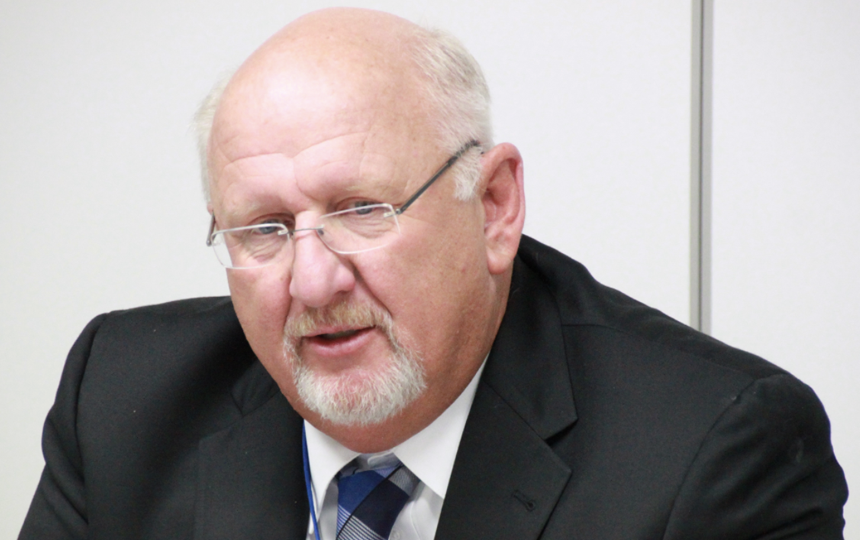
Former Senior Executive Positions of U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission, with over 45 years of
experience in nuclear operations, regulation, and oversight, Dr. Casto was a first responder to
Japan in 2011, providing support during the Fukushima crisis. He is committed to ensuring the
highest standards of nuclear safety and reliability at TEPCO.

Additionally, from March 25 to April 2, 2024, international nuclear security specialists selected
under IAEA visited KNPS for an expert mission which is review of nuclear facilities and activities
of operators in IAEA member countries in accordance with IAEA international standards.
They checked an improvement of physical protection of nuclear materials against international
nuclear security instruments established by the IAEA. The report specifically commended the
management team's efforts to foster a stronger nuclear security culture at KNPS. However, it also
outlined areas where further improvements are needed, with key recommendations that included:
TEPCO has committed to incorporating these recommendations into its broader defense-in-depth strategy, ensuring that KNPS remains on a path of continuous improvement in nuclear security, enhancing safety and resilience with each step forward.
Many individuals, including distinguished guests and key figures from around the world, have visited the Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Station (KNPS).
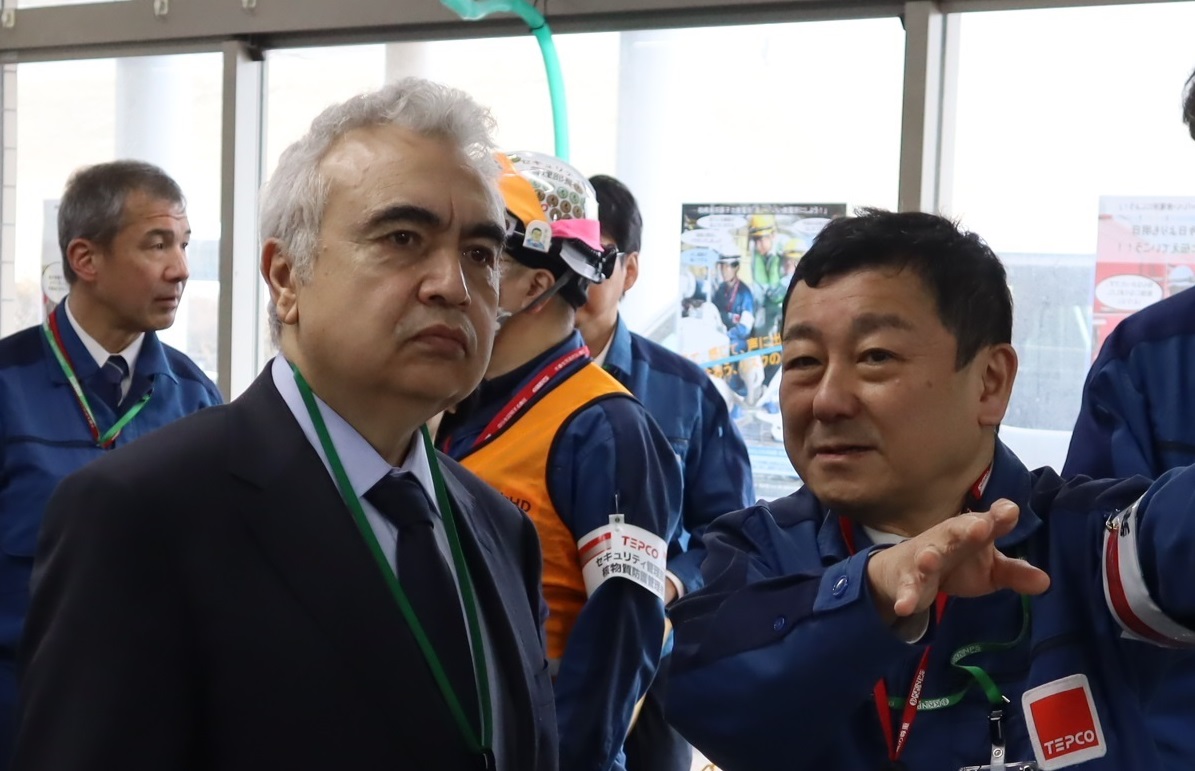
Dr. Fatih Birol, visited KNPS on March 26, 2025 and praised the high level of safety awareness with which everyone involved is working. Emphasizing that the active use of nuclear power is essential for Japan to maintain its energy security, achieve economic growth, and combat climate change, Dr. Birol expressed hope that the plant would be restarted as soon as possible, in line with safety standards and regulatory requirements.

Former U.S. Ambassador Rahm Emanuel's visit on November 21, 2024, provided a powerful endorsement of KNPS's ongoing safety enhancements. His remarks emphasized the importance of embracing lessons from past challenges, integrating them into new operational protocols, and continuously refining practices. His observations highlight the critical role of adaptive learning in fostering a safe and forward-looking nuclear environment, echoing the commitment that has guided improvements at KNPS for nearly 15 years.

Building on the lessons learned from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Accident, KNPS has implemented a wide array of infrastructural upgrades and operational safeguards designed to withstand extreme events. These enhancements demonstrate a robust defense-in-depth strategy that protects the facility against a diverse range of risks.
For a more in-depth look at the specific safety measures and protocols in place at KNPS, please visit our detailed Safety Measures page
Ambassador Julia Longbottom's visit on August 19, 2024, further underscores the global confidence in KNPS's safety and operational excellence. Her observations highlighted the professionalism and dedication of the KNPS team and reinforced the vital role of nuclear power as a low-carbon energy source in the fight against climate change. Her comments serve as a powerful reminder that the rigorous safety measures at KNPS not only protect the facility and its personnel but also contribute to broader environmental and societal goals.

The extensive independent reviews, the IAEA expert mission and international visits highlight KNPS's advancements in nuclear safety. These inspections, combined with the commitment of entire TEPCO team, underscore the station's readiness to play a pivotal role in Japan's energy. Overall, the NRMC review, held in May 2024, confirmed that critical safety issues have been addressed, with the station on track for a safe restart. While the March 2024 IAEA mission identified areas for further improvement, such as raising security standards and operational practices, these insights reflect TEPCO's commitment to continuous progress, with the feedback being integrated into the station's evolving safety measures. With no significant nuclear safety issues identified, and with a strong safety culture and robust operational practices in place, TEPCO's dedication to progress is evident across all facets of KNPS's operations. Through continuous training, cutting-edge infrastructure, and a transparent approach to safety, KNPS supports Japan's energy future. Looking forward, KNPS will remain a model for best practices, ensuring its pivotal role in energy security, economic stability, and environmental sustainability.

The Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Station stands as a testament to Japan's resilience and innovation in the energy sector.

The Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Accident, while tragic, was a catalyst for TEPCO’s adoption of a defense-in-depth strategy, emphasizing a layered approach to nuclear safety.

By continuously evaluating and upgrading safety protocols, KNPS demonstrates its dedication to upholding the highest standards of nuclear safety, ensuring a safe and sustainable future.

Independent assessments by Japanese and international experts reaffirm TEPCO's commitment to transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement.
Contents